Difference between revisions of "Flow Limitation"
Sleeprider (talk | contribs) (Created page with "Flow limitation may be inspiratory (during inhale) or expiratory (during exhale). It refers to any condition which impares the flow-rate of air through the respiratory tract....") |
Sleeprider (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
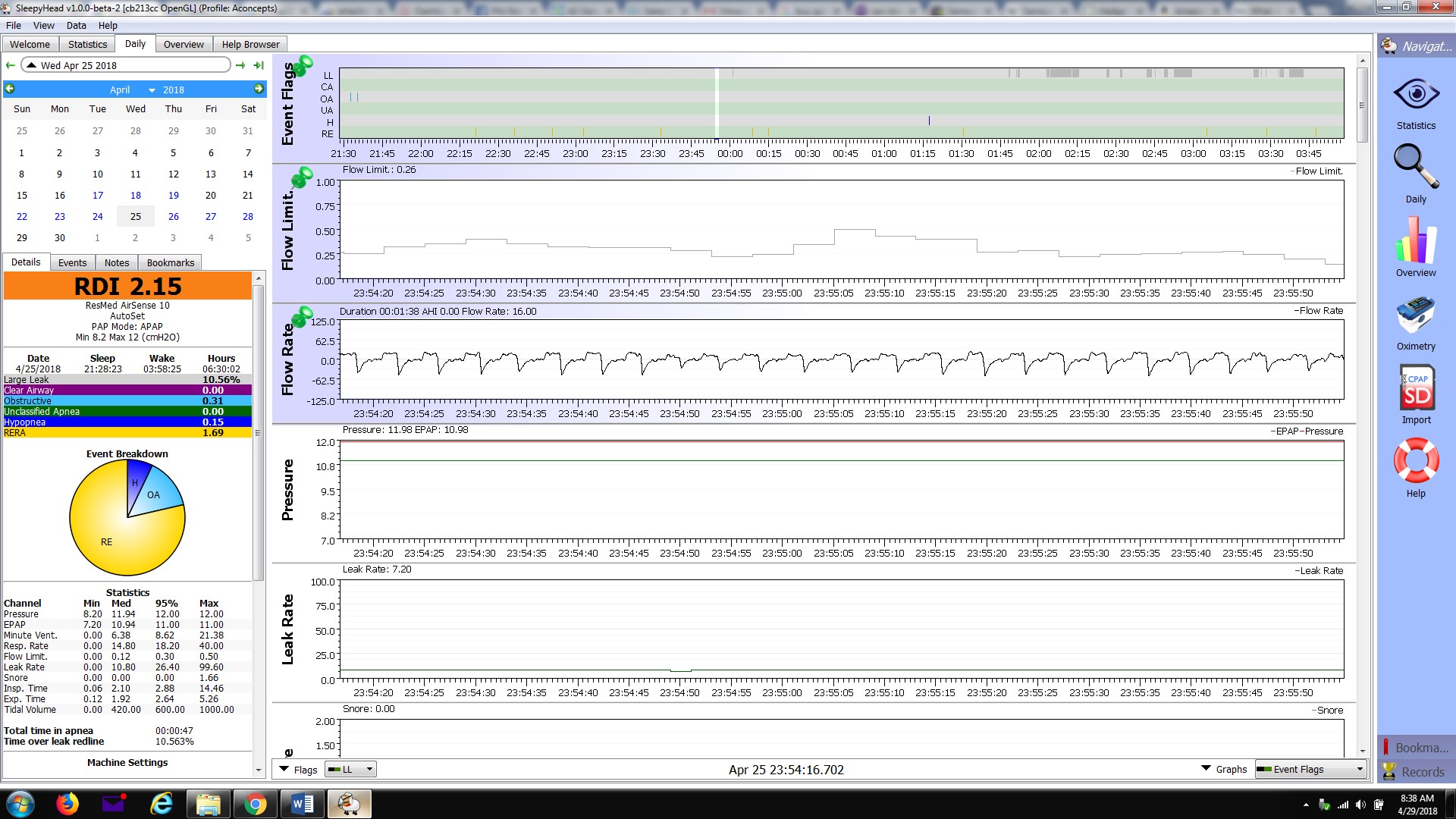
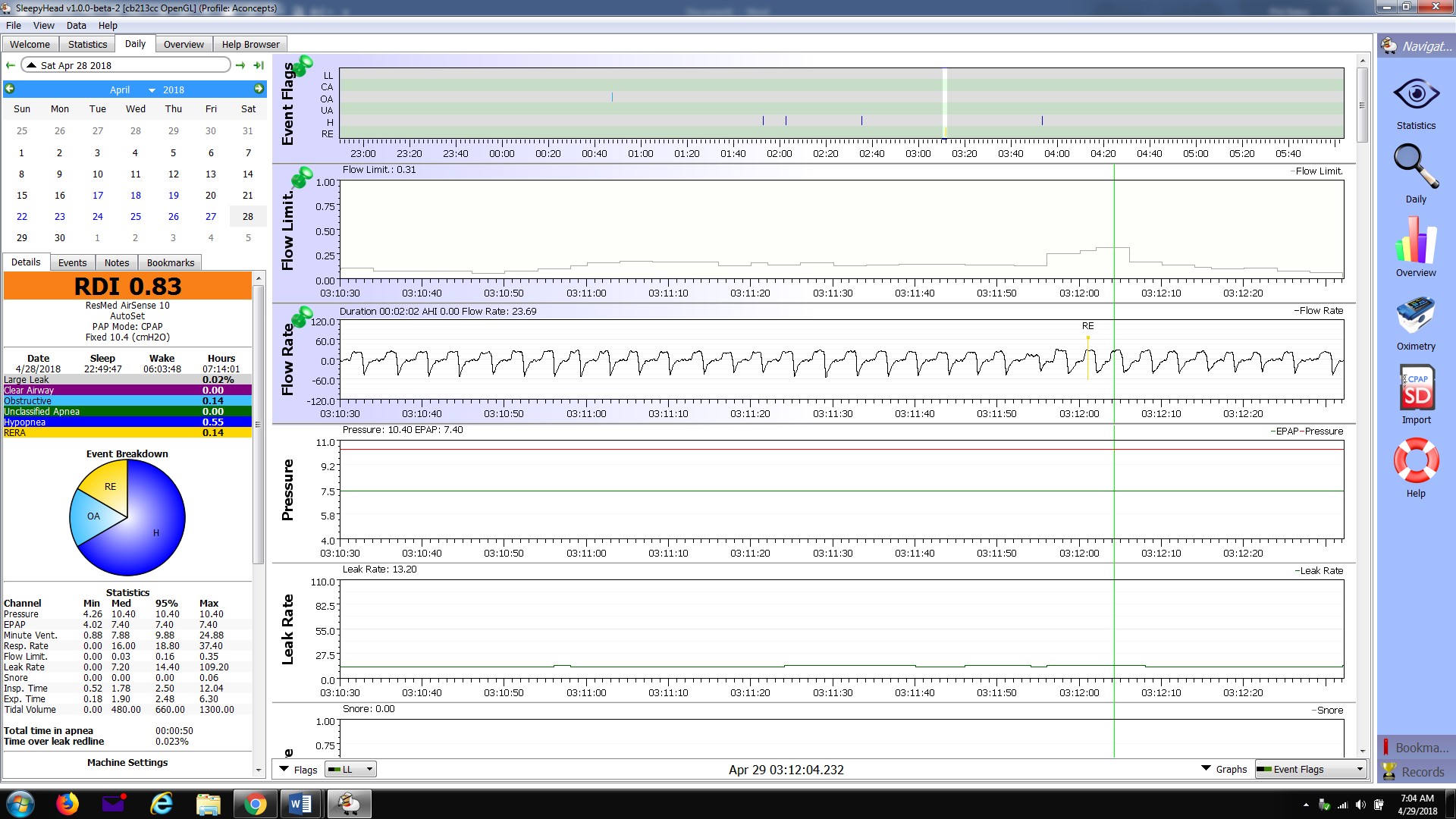
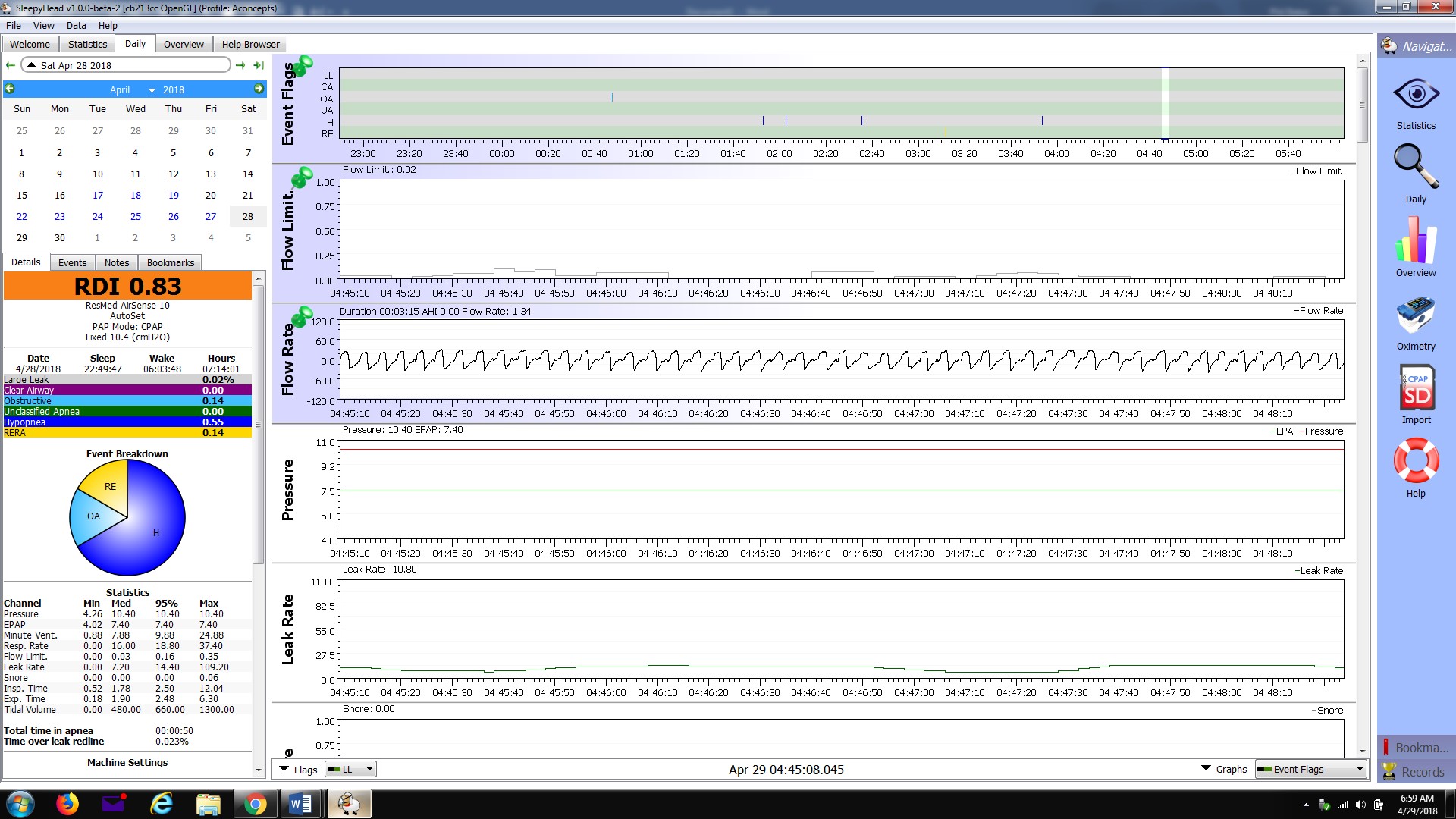
Flow limitation may be inspiratory (during inhale) or expiratory (during exhale). It refers to any condition which impares the flow-rate of air through the respiratory tract. Inspiratory Flow limitations occur to many individuals that are diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea. Inspiratory Flow Limitation (IFL) is an increasing resistance in inspiratory flow that slows the volume and flow of air as the inhale proceeds. It is visualized in a flow rate graph as a flattened or downward sloping wave-form rather than a smooth peak. Expiratory Flow Limitation (EFL) is similarly restricted flow rate during the exhale cycle. Flow limitations can result from anatomical narrowing of the airway, airway obstruction, and positional obstruction where the airway is restricted due to an individual's sleep position resulting in occlusion of the airway. EFL may also result from an intolerance to CPAP pressure during exhale. Both IFL and EFL seem to respond well to bilevel therapy where the exhale positive air pressure (EPAP) is a lower pressure than the inhale positive air pressure (IPAP). | Flow limitation may be inspiratory (during inhale) or expiratory (during exhale). It refers to any condition which impares the flow-rate of air through the respiratory tract. Inspiratory Flow limitations occur to many individuals that are diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea. Inspiratory Flow Limitation (IFL) is an increasing resistance in inspiratory flow that slows the volume and flow of air as the inhale proceeds. It is visualized in a flow rate graph as a flattened or downward sloping wave-form rather than a smooth peak. Expiratory Flow Limitation (EFL) is similarly restricted flow rate during the exhale cycle. Flow limitations can result from anatomical narrowing of the airway, airway obstruction, and positional obstruction where the airway is restricted due to an individual's sleep position resulting in occlusion of the airway. EFL may also result from an intolerance to CPAP pressure during exhale. Both IFL and EFL seem to respond well to bilevel therapy where the exhale positive air pressure (EPAP) is a lower pressure than the inhale positive air pressure (IPAP). | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[file:FL EPR.jpg]] |
| − | [[ | + | [[file:FL EPR 3 moderate.jpg]] |
| − | [[ | + | [[file:FL EPR 3 Good.jpg]] |
Revision as of 02:29, 2 May 2018
Flow limitation may be inspiratory (during inhale) or expiratory (during exhale). It refers to any condition which impares the flow-rate of air through the respiratory tract. Inspiratory Flow limitations occur to many individuals that are diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea. Inspiratory Flow Limitation (IFL) is an increasing resistance in inspiratory flow that slows the volume and flow of air as the inhale proceeds. It is visualized in a flow rate graph as a flattened or downward sloping wave-form rather than a smooth peak. Expiratory Flow Limitation (EFL) is similarly restricted flow rate during the exhale cycle. Flow limitations can result from anatomical narrowing of the airway, airway obstruction, and positional obstruction where the airway is restricted due to an individual's sleep position resulting in occlusion of the airway. EFL may also result from an intolerance to CPAP pressure during exhale. Both IFL and EFL seem to respond well to bilevel therapy where the exhale positive air pressure (EPAP) is a lower pressure than the inhale positive air pressure (IPAP).

Donate to Apnea Board